Codec performance test results
The following codec performance test was performed on Ozeki VoIP SIP SDK v9.7.0 on 2012.04.13. The test was setup to verify how many simultaneous SIP/VoIP calls can be established by a standard workstation running an application based on Ozeki VoIP SIP SDK.
The test was executed using the following workstation(s):
Model: Dell Vostro 430 OS: Windows 7 enterprise Processor: Intel(R) Core (TM) i7 CPU 860 @ 2.80 Ghz 2.80 Ghz Installed memory (RAM): 4.00 GB System type: 64 bit Operating System
The software environment consisted of the Ozeki Phone System PBX, and
custom test applications based on the Ozeki VoIP SIP SDK Softphone demo.
During all tests minimal load was experienced on the PBX system. Hint: The
Ozeki Phone System PBX is also based on the Ozeki VoIP SIP SDK. It can
be downloaded form www.ozekiphone.com.
During each test "Test Client A" made several calls to "Test Client B",
and one call was randomly routed to a "human test point". At each
test client an automated voice quality verification module
was used to detect system breakdown, by evaluating packet latency and
the bit rate after decoding. A call was treated acceptable, as long
as sufficient bitrate was produced by the codec to provide continuous
audio playback.
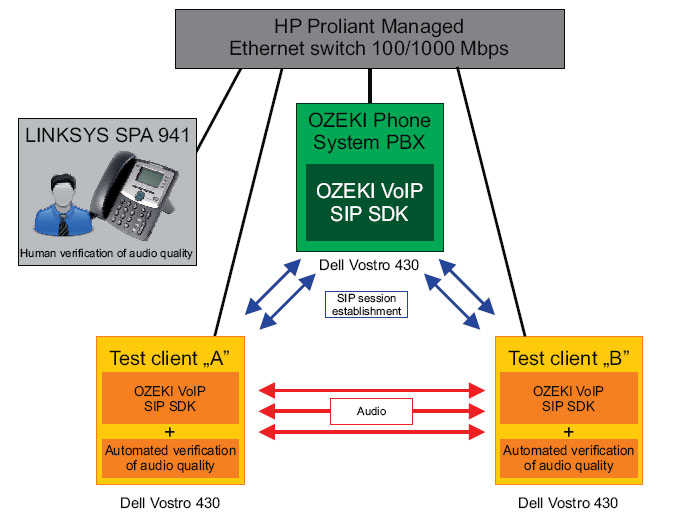
The test application was used to create as many calls in a loop as fast as possible.
Test results
| Codec name | Max simultaneous calls limited by CPU | Max number of calls on 100MBps LAN | Max number of calls on 1000MBps LAN | Bandwidth (kbs) | packets/s | sample interval (ms) | Raw data size | Enc data size | Compression (%) |
| Alaw | 31250 | 656 | 6564 | 78 | 50 | 20 | 320 | 160 | 50 |
| Ulaw | 36363 | 656 | 6564 | 78 | 50 | 20 | 320 | 160 | 50 |
| G722 | 679 | 656 |
679 (limited by CPU) 6564 (theoritical) |
78 | 50 | 20 | 320 | 160 | 50 |
| G723-30 | 1374 |
1374 (limited by CPU) 3103 (theoritical) |
1374 (limited by CPU) 31030 (theoritical) |
16,5 | 33,3 | 30 | 480 | 24 | 95 |
| G726-16000 | 1811 | 1641 |
1811 (limited by CPU) 16410 (theoritical) |
31,2 | 50 | 20 | 320 | 40 | 87,5 |
| G726-24000 | 1984 | 1313 |
1984 (limited by CPU) 13128 (theoritical) |
39 | 50 | 20 | 320 | 60 | 81,25 |
| G726-32000 | 1964 | 1094 |
1964 (limited by CPU) 10940 (theoritical) |
46,8 | 50 | 20 | 320 | 80 | 75 |
| G726-40000 | 1821 | 938 |
1821 (limited by CPU) 9377 (theoritical) |
54,6 | 50 | 20 | 320 | 100 | 68,75 |
| G728 | 345 |
345 (limited by CPU) 1641 (theoritical) |
345 (limited by CPU) 16410 (theoritical) |
31,2 | 50 | 20 | 320 | 40 | 87,5 |
| G729 | 510 |
510 (limited by CPU) 2188 (theoritical) |
510 (limited by CPU) 21880 (theoritical) |
23,4 | 50 | 20 | 320 | 20 | 93,75 |
| Speex-narrowband | 83 |
83 (limited by CPU) 1932 (theoritical) |
83 (limited by CPU) 19321 (theoritical) |
26,5 | 50 | 20 | 320 | 28 | 91,25 |
| ILbc-30 | 173 |
173 (limited by CPU) 2207 (theoritical) |
173 (limited by CPU) 22069 (theoritical) |
23,2 | 33,3 | 30 | 480 | 50 | 89,58333333 |
| GSM | 1059 |
1059 (limited by CPU) 1829 (theoritical) |
1059 (limited by CPU) 18286 (theoritical) |
28 | 50 | 20 | 320 | 33 | 89,6875 |
Explanation
Max simultaneous calls: Measured raw codec performance. Theoretical maximum number
of calls on this hardware. Measured number of encoding/decoding cycles per second
divided by the number of packets to be encoded per second for the given codec.
N = 1 second / ((Time required for encoding + time required for decoding) * (number of packets needed for the given codec/second))
Max number of calls on 100MBps LAN: The number of calls that can operate simultaneously if
"Test Client A" and "Test Client B" reside on different workstations and they are
connected with a 100 Mbps LAN and we use two way audio.
Max number of calls on 1000MBps LAN: The number of calls that can operate simultaneously if
"Test Client A" and "Test Client B" reside on different workstations and they are
connected with a 1 Gbps LAN and we use two way audio..
Bandwidth (kbs): Bandwidth requirement of a single call (two way audio)
Packet/s: The number of RTP packets transmitted per second to deliver audio.
Sample interval(ms): The length of audio date in a packet
Raw data size: The size of the digitized audio packet before encoding (in octets), assuming
8 khz, 16 bit, mono audio stream.
Encoded data size: The size of the audio packet after encoding.
Compression (%): The compression rate of the codec. The size of the audio packet after encoding
divided by the size of the audio packet before encoding
Findings
Each codec requires different CPU processing power for encoding and decoding. For most codecs
the maximum number of calls is limited by the CPU processing capability. For high performance
systems operating in a LAN environment, we highly recommend the G711 uLaw codec.
During our tests the Ozeki PBX server never experienced high load.
