Integrated Services Digital Network (ISDN) lines
ISDN stands for Integrated Services Digital Network. It includes a range of communications standards for simultaneous digital transmission of voice, data, video or other services over the public switched telephone network.
ISDN is a circuit-switched telephone network system that also allows access to packet switched networks. It has been developed to ensure voice and data transmissions over traditional lines digitally. This results in a higher voice quality than in case of analog lines (Figure 1).
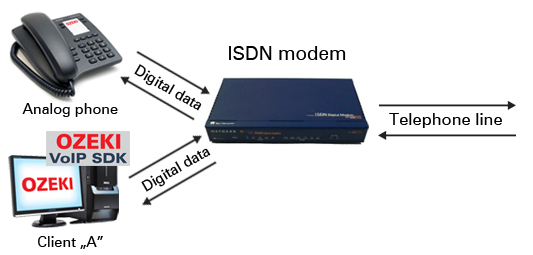
ISDN lines provide circuit-switched connections for either voice or data, and packet-switched connections for data. If it is used for Internet access, ISDN provides a maximum of 128 kbit/s in both upstream and downstream directions.
Due to "integrated services", ISDN lines can allow to deliver data (in any combination of data, voice, video, and fax) at minimum two simultaneous connections over a single line. It is also possible to connect multiple devices to the line if it is required. In this way, since ISDN lines offers more features than analog ones, they can completely satisfy the communications needs of most people at a higher transmission rate.
The main advantage of ISDN is the ability of integrating speech and data on the same line and adding further features not available in the traditional telephone system. Analog telephones and fax machines can also be used over ISDN lines but their signals are converted into digital signal.
Channels
ISDN employs 64 kbps channel (B) (bearer) to carry voice and data. Channel (D) (delta) is used for control. It is referred to as signaling channel since it signals the carrier's voice switch in order to make calls, put them on hold and activate additional features such as conference calling or call forwarding. Also due to the fact that channel (D) allows direct connection to the telephone system's SS7 signaling network, ISDN telephone calls are much faster than regular phone calls.
Basic Service
ISDN BRI is short for Basic Rate Interface uses one wire pair for providing two 64 Kbps B channels and one 16 Kbps D channel. Channels B are for voice or data and channel D is used for any combination of data, control or signaling, as well. Channels B are often added and providing in this way a data rate of 128 kbps.
High-Speed Service
ISDN PRI stands for Primary Rate Interface. It uses four wire pairs to provide 23 B channels and one 64 Kbps D channel.
